Introduction
The food service industry is a significant contributor to the global economy, employing millions worldwide. Within this sector, companies like McDonald's and Starbucks play important roles, not only because of their large market share but also in setting industry standards for employment practices. The food service industry also faces ongoing scrutiny regarding wage practices and the quality of food being served. This issue will explore the financial and employment practices of McDonald's and Starbucks, two large public companies in this sector, to assess their approaches to employee compensation and benefits.
Industry Overview
The food service industry encompasses a wide range of establishments, from quick-service restaurants to specialty coffee shops. In recent years, this industry has faced challenges such as fluctuating consumer preferences, economic downturns, and labor shortages. Despite these hurdles, leading companies have demonstrated resilience through strategic growth and robust financial management thereby rewarding their shareholders handsomely. However, questions remain on how they treat employees and the environment - two areas of focus for companies we are researching and will be presenting in this article.
McDonald's Corporation
Financial Performance
Over the past five years, McDonald's has shown consistent financial growth. According to the company's 2023 Annual Report, global revenues increased from $21.0 billion in 2019 to $23.2 billion in 2023, marking a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2.5% (SEC). Net income also rose from $6.0 billion in 2019 to $7.5 billion in 2023, reflecting a CAGR of about 5.7%. McDonald's has maintained high profitability in the last decade, with an average gross margin of 40% and a net profit margin of 25%. Its franchising model reduces operational costs, yielding a return on equity (ROE) of 40%. The company prioritizes shareholder returns and distributes profits through dividends and stock buybacks.
Workforce Composition
As of December 31, 2023, McDonald's employed approximately 200,000 individuals globally, with around 60% working in company-operated restaurants and the remainder in corporate roles (SEC.) The majority of employees are part-time, reflecting the industry's reliance on flexible labor to meet variable demand. While flexibility is essential in running a good operation, the impact of part-time work, unpredictable hours and no benefits makes the livelihood for the part-time employee very difficult. This is something that employers and public policy makers should rectify given the large number of such employees in the food service industry.
Wage Structure
McDonald's wage policies vary by region, influenced by local labor laws and market conditions. In the United States, the company has committed to raising the average hourly wage to $15 by 2024 for employees in company-owned restaurants (Jobcase). However, wages in franchised locations, which constitute a significant portion of McDonald's outlets, are determined by individual franchisees and may differ from corporate standards. As minimum wages vary across the country, the wage rates for franchise operations are not consistent with McDonald’s target wages - both for full-time and part-time employees.
Employee Benefits
McDonald's offers a range of benefits to its full-time employees, including health insurance, paid time off, and educational assistance. Full-time employees are eligible for comprehensive health coverage, while part-time employees may have access to limited benefits, depending on their hours worked and tenure (McDonald's). The company also provides tuition assistance programs, such as the Archways to Opportunity initiative, that supports employees pursuing higher education. Since part-time employees make up the majority of McDonald’s employees, a large number of workers do not have access to these benefits.
Starbucks Corporation
Financial Performance
Starbucks has experienced robust financial growth in the past five years. The company's 2023 Annual Report indicates that revenues increased from $26.5 billion in 2019 to $35.0 billion in 2023, achieving a CAGR of approximately 7.1% (SEC). Net income grew from $3.6 billion in 2019 to $4.5 billion in 2023, reflecting a CAGR of about 5.7%. Overall, the company has witnessed significant revenue growth in the last decade due to global expansion and innovative global offerings. Starbucks has chosen to reinvest profits in marketing and R&D to enhance customer experience and business growth. This however has resulted in about 30% lower gross margin of about 30% and 10% lower net profit margin compared with McDonald's over 10 years till 2023.
Workforce Composition
As of October 1, 2023, Starbucks employed approximately 400,000 individuals worldwide, with the majority working in company-operated stores (SEC). The workforce comprises both full-time and part-time employees, with a significant number of part-time “partners” (as Starbucks refers to its employees).
Wage Structure
Starbucks has implemented progressive wage policies, aiming to provide competitive compensation across its markets. In the United States, the company announced plans to increase the starting wage to $15 per hour by 2023, with an average hourly wage of $17 (Starburst Magazine). These wage increases apply to both full-time and part-time employees, reflecting Starbucks' commitment to equitable pay.
Employee Benefits
Starbucks offers an extensive benefits package to its employees, including health insurance, stock options, and educational opportunities. Notably, both full-time and part-time employees who work a minimum of 20 hours per week are eligible for health benefits (Starbucks Careers). The company also provides the Starbucks College Achievement Plan, offering full tuition coverage for a bachelor's degree through Arizona State University's online programs (Starbucks).
Comparative Analysis
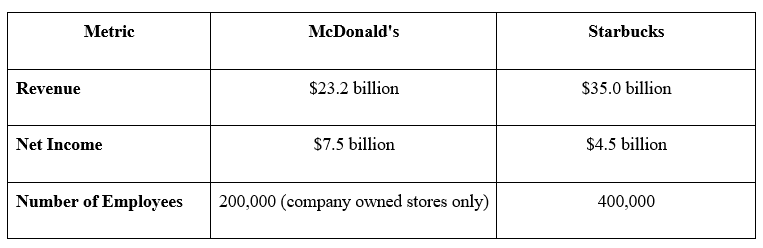
Financial Metrics - 2023
Sources: McDonald's 2023 Annual Report, SEC McDonalds, SEC Starbucks
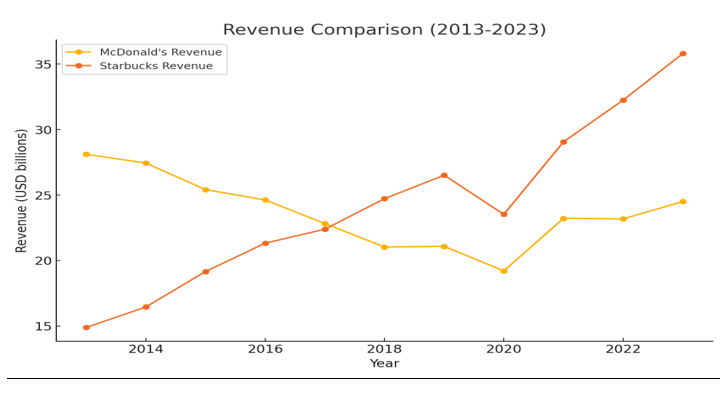
Sources: Annual Reports 2013 to 2023
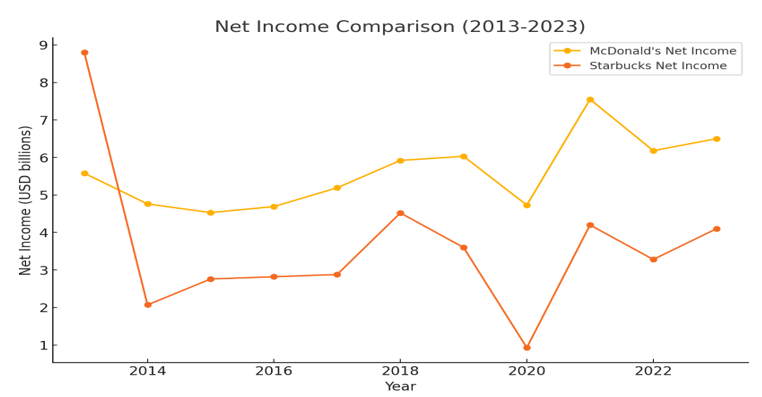
Sources: Annual Reports 2013 to 2023
The graphs above depict the trends for both companies over the ten years 2013 to 2023. It shows that Starbucks' revenue grew steadily, but McDonald's profitability ratios is consistently higher, illustrating how these two companies prioritize their investment in growth, employees and shareholders with clear differences between these two companies.
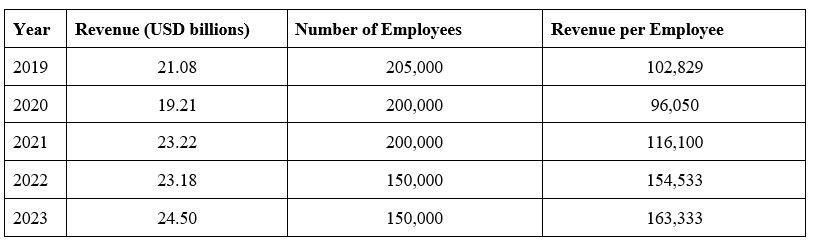
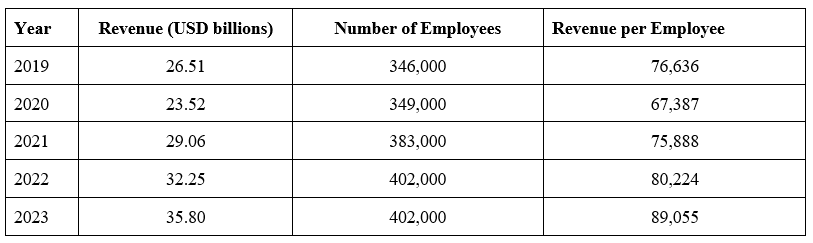
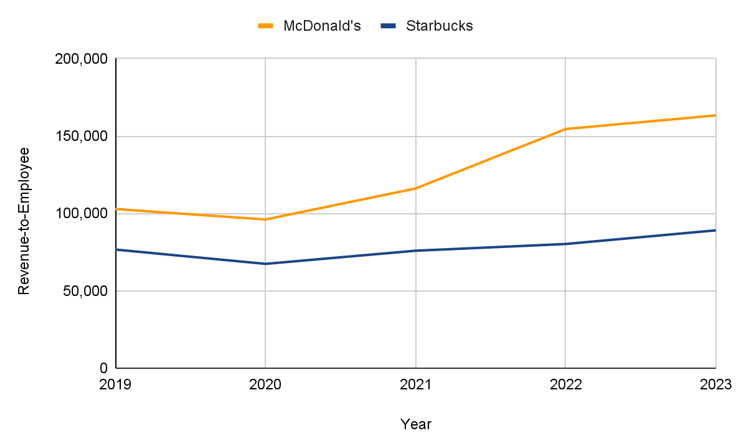
Revenue-to-Employee 5-year comparison
McDonald’s
Source: Annual Reports (2019-2022) and reported annual fillings (employee numbers)
Starbucks
Source: Annual Reports (2019-2022) and official company disclosure (employee numbers)
Source: Annual Reports (2019-2022), reported annual fillings, and official company disclosure
McDonald’s higher revenue per employee number is primarily driven by expanding growth through franchising. The extra revenue from franchising is then spread over its own workforce rather than the total workforce employed in the McDonald system (including franchises). Starbucks productivity measured by revenue per employee appears to be real productivity gains reflected by its investment in employees in terms of wages, benefits and education/training.
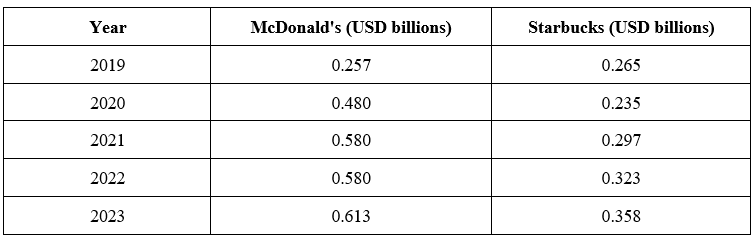
Marketing, advertising, and sales expenses
Source: LSEG Workspace
McDonald's typically includes marketing and advertising expenses within its Selling, General, and Administrative (SG&A) expenses which can be disclosed separately. Estimates however suggest that marketing and advertising expenses account for approximately 2.5% of McDonald’s total revenue. Franchise spending on advertising is not included in the total advertising cost so McDonald’s advertising cost is underestimated. Starbucks however, includes marketing and advertising as part of operating expenses. This is estimated to be about 1% of total revenue.
Wage and Benefits Comparison
Both companies have committed to raising starting wages to $15 per hour in the U.S. McDonald's wage commitments primarily apply to company-owned restaurants, with franchised locations setting their own wage standards. Starbucks' policy extends this wage increase to both full-time and part-time employees. In terms of benefits, Starbucks offers more inclusive health coverage and educational opportunities to part-time employees compared to McDonald's, which limits benefits available to part-time staff.
McDonald’s generated $8.5B in net income in 2023 and paid out $7.6B in dividends and share repurchase while Starbucks generated $4.1B in net income in 2023 and paid out $3.4B in dividends and share repurchase.
In future articles, we will explore more on how shareholder supremacy and profit maximization pushes companies and their leadership to rewards shareholders mores (by implication themselves as they are major shareholders) to the exclusion of employees, the planet and other stakeholders.
References
● McDonald's Corporation. (2023). Annual Report. Retrieved from SEC
● Starbucks Corporation. (2023). Annual Report. Retrieved from SEC
● Starbucks Careers. (2023). Benefits. Retrieved
● Jobcase. (2024). Jobcase
● https://careers.starbucks.com/benefits/
● https://starbmag.com/what-are-the-benefits-of-working-at-starbucks/